Thunk middleware
Redux doesn’t allow any side effects in its reducer functions, preventing developers to encapsulate the whole application logic in a single place. SemTUI makes use of a particular middleware layer, introduced between an action dispatcher and a reducer function, allowing to execute any side effects before reaching a reducer. This middleware layer is called Thunk, which means that a piece of code is still working, even if it does some delays: rather than executing some logic now, a function can be called to perform an action later on. In Redux specifically, thunks are a pattern which encapsulates logic, including asynchronous logic, inside functions that can interact with the global store through other action dispatchers and slices of the state.
Earlier, a schema describing the data flow between React components and the Redux global store has been presented. When async logic is added to the workflow, an extra step is added where a middleware can run logic like AJAX requests and dispatch results to a reducer, updating the store.
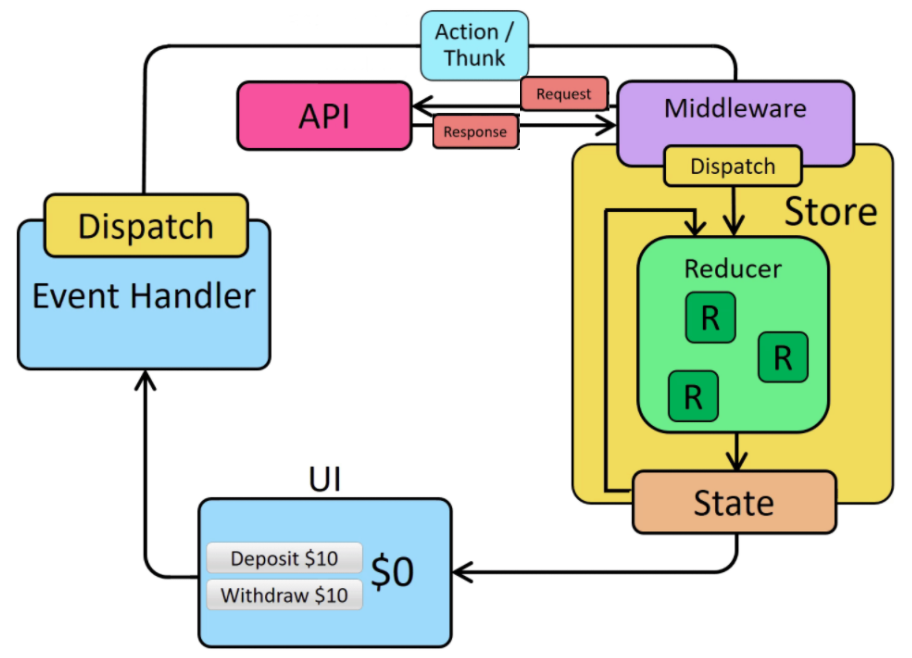
As a framework, SemTUI builds on top of thunks to support future thunk actions, exposing for each of them a status of loading, error and fullfilled. Each status can be mapped to a specific reducer function allowing to be automatically executed based on the async request result. Those statuses are also available to be requested by a component through a normal redux selector.
The API layer is also built to be expandable with additional API endpoints through a configuration file. The path for each specified endpoint is parsed to substitute possible additional dynamic parameters. For example, let’s imagine to reconcile a set of selected labels cells of the currently loaded table. The steps to complete the process are the following:
- multiple actions (SELECT CELL) are dispatched when a select event occurs;
- a reducer function takes as input the id of a cell and updates the state to set the cell to selected. This step will be repeated each time an action SELECT CELL will be fired;
- once the user has selected all of the desired table cells, a thunk action can be initiated to query a specific reconciliator endpoint;
- the thunk middleware receives the action payload with the currently selected cells and queries a reconciliation endpoint;
- the reconciliation endpoint, e.g.: RECONCILE ASIA, is previously defined where the path to it is specified;
- if the request fails, the error is automatically handled by the framework, so that no additional code is required when additional endpoints are added;
- if the request fullfills without errors, a reducer function is mapped to this state and will be automatically executed to update the selected cells with the annotation metadata obtained from the reconciliator service;
- finally, a selector, which was previously defined to select the table data, has some of the dependencies changed (some cells got updated) and the value is recomputed and returned to the component responsible to rerender the current view of the table.
info
If the result of an API endpoint doesn’t affect the global state, the endpoint can be directly queried from a component through the API layer without defining any thunk action.
APIs configuration
The APIs can be defined in the config.ts situated in the root of src directory:
const CONFIG: AppConfig = {
API: {
// global endpoint prefixed to each path, unless useGlobal is set to false
GLOBAL: process.env.REACT_APP_BACKEND_API_URL || '',
ENDPOINTS: {
GET_SERVICES_CONFIG: {
path: '/config',
// prefix global endpoint to /config. If not specified it defaults to true
useGlobal: true
},
GET_DATASET: {
path: '/dataset'
},
GET_TABLE: {
path: '/dataset/:datasetId/table/:tableId'
},
DELETE_DATASET: {
path: '/dataset/:datasetId'
},
...
}
}
};
Endpoints can then be used to build an async function which can then be executed to query the specified endpoint. The endpoints function are situated in the services directory:
// an API object includes a set of async function to query the endpoints previously defined
const datasetAPI = {
getDataset: (params: Record<string, string | number> = {}) => {
return apiClient.get<GetCollectionResult<Dataset>>(apiEndpoint({
// name of object of the configuration
endpoint: 'GET_DATASET',
}), { clearCacheEntry: true });
},
uploadDataset: (formData: FormData) => {
return apiClient.post(
apiEndpoint({
endpoint: 'UPLOAD_DATASET'
}),
formData
);
},
deleteDataset: (datasetId: string) => {
return apiClient.delete(
apiEndpoint({
endpoint: 'DELETE_DATASET',
// to specify parameters. Parameters are prefixed by ':'
// For exammple /dataset/:datasetId will be transformed to /dataset/[valueOfTheVariableDatasetId]
paramsValue: { datasetId }
})
);
},
...
};
Thunk definition
APIs functions can the be used in a thunk defined in a *.thunks.ts of a store slice:
const ACTION_PREFIX = 'dataset';
export enum DatasetThunkActions {
GET_DATASET = 'getDataset',
...
}
export const getDataset = createAsyncThunk(
`${ACTION_PREFIX}/${DatasetThunkActions.GET_DATASET}`,
async () => {
const response = await datasetAPI.getDataset();
return response.data;
}
);
ACTION_PREFIX: each slice thunk has a prefix manually defined by the developer.GET_DATASET: is an enum defining the name of the action. It is important to define it to keep track of the status of async operation.
Thunk statuses
Each thunk when executed has three states:
- pending: the async operation is currently pending;
- fullfilled: the async operation terminated without errors;
- error: the async operation terminated with some errors;
A selector can be built to retrieve the status of the request:
export const selectGetDatasetStatus = createSelector(
selectRequests,
(requests) => getRequestStatus(requests, DatasetThunkActions.GET_DATASET)
);
And then can be used, like any other selector, inside a component:
const SomeComponent = () => {
const dispatch = useAppDispatch();
const { pending, error } = useAppSelector(selectGetDatasetStatus);
const onClick = () => {
dispatch(getDataset());
},
// if request is pending
if (pending) {
return <div>Loading...</div>
}
// if request returned any error
if (error) {
return <div>{error[0].status}</div>
}
// if request fullfilled
return (
...
)
}
Mapping thunk statuses to reducers
You can directly map a request status to a reducer function of a slice, so that the state of the slice can be updated automatically when the status changes:
export const datasetsSlice = createSliceWithRequests({
name: 'datasets',
initialState,
reducers: {
// normal reducers
...
},
// reducers mapped to thunk statuses
extraRules: (builder) => (
builder
// on thunk request fullfilled update datasets
// (getDataset is the thunk action exported from the dataset.thunks.ts)
.addCase(getDataset.fulfilled,
(state, action: PayloadAction<GetCollectionResult<Dataset>>) => {
const { meta, collection } = action.payload;
state.entities.metaDatasets = meta;
state.entities.datasets = collection
.reduce<DatasetsInstancesState>((acc, { id, ...rest }) => {
acc.byId[id] = {
id,
tables: [],
...rest
};
acc.allIds.push(id);
return acc;
}, { byId: {}, allIds: [] });
})
.addCase(...)
...
)
});