Introduction
In the I2T framework, a Service Category defines a functional class of modules that can interact with the system through a standardized interface. Each category groups services that share a similar purpose and follow a common input/output structure, allowing the framework to manage them uniformly through the External Service Aggregator.
Existing categories include:
- Reconcilers – Services responsible for aligning or enriching metadata by matching entities with external sources (e.g., linking local data to external knowledge bases).
- Extenders – Services that add complementary data or attributes to existing resources, by fetching related information from external systems.
- Modifiers – Services that process and transform data, such as formatting, normalization, anonymization or restructuring operations applied to a column.
Server startup
As soon as the server spins up, all described services are parsed and validated against a schema. An unsuccessful parsing of a service will result in a validation error. Invalid services won't be available at runtime.
The user will be prompted with the following information on startup:
Reconciliators
✖ service1
Errors:
1. detailed validation error
✔ service2
✔ service3
✔ service4
Extenders
✔ service1
✔ service2
✔ service3
Modifiers
✔ service1
✔ service2
✔ service3
Query an external service
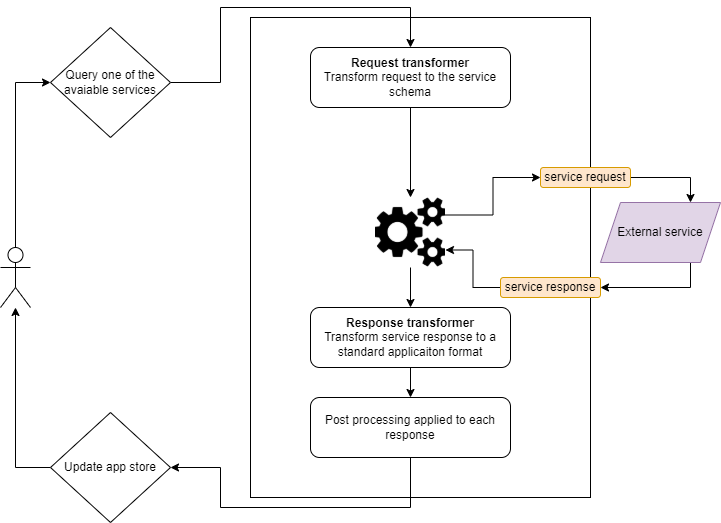
Once a client connects to the server, a configuration for all the supplied services is sent to the client where it is parsed, displaying available services and their settings to the user. When a request to a service is sent from the client to the server, a pipeline executes the transformation functions specified to query the service and return its result. An additional post processing is applied to the final response to compute some statistics necessary for the application. The post processing is placed on top of the transformation functions provided by the user, so that further services additions do not need to explicitly tell the system how to compute those statistics.
info
Two different pipeline exists for reconciliators, extenders and modifiers services. They can be found in
./api/services/extension/extension-pipeline.js, ./api/services/reconciliation/reconciliation-pipeline.js
and ./api/services/modification/modification-pipeline.js.
Adding a new Service Category
This section serves as a guide for future developers who may need to introduce a new Service Category. It indicates the required steps to integrate the new category both in the backend (core logic, API, configuration) and in the frontend (UI representation and interaction).
Backend Integration
📦src
┣ 📂api
┃ ┣ 📂controllers
┃ ┃ ┣ 📜config.controller.js
┃ ┃ ┗ 📜newCategoryService.controller.js
┃ ┣ 📂routes
┃ ┃ ┣ 📜index.js
┃ ┃ ┗ 📜newCategoryService.route.js
┃ ┣ 📂middleware
┃ ┃ ┗ 📜logger.js
┃ ┗ 📂services
┃ ┣ 📂logger
┃ ┃ ┗ 📜logger.service.js
┃ ┗ 📂newCategoryService
┃ ┣ 📜newCategoryService-pipeline.js
┃ ┗ 📜utils.js
┣ 📂config
┃ ┗ 📜index.js
┗ 📂services
┗ 📂newCategoryService
Frontend Integration
📦src
┣ 📂components
┃ ┗ 📂core
┃ ┗ 📂DynamicForm
┃ ┗ 📜DynamicForm.tsx
┣ 📂pages
┃ ┗ 📂Viewer
┃ ┗ 📂TableViewer
┃ ┣ 📂Menus
┃ ┃ ┗ 📂ContextMenus
┃ ┃ ┗ 📜ContextMenuColumn.tsx
┃ ┣ 📂NewCategoryServiceDialog
┃ ┣ ┗ 📜NewCategoryServiceDialog.tsx
┃ ┗ 📂SubToolbar
┃ ┗ 📜SubToolbar.tsx
┣ 📂services
┃ ┗ 📂api
┃ ┗ 📜table.ts
┗ 📂store
┗ 📂slices
┣ 📂config
┃ ┣ 📂interfaces
┃ ┃ ┗ 📂config.ts
┃ ┣ 📜config.selectors.ts
┃ ┗ 📜config.slice.ts
┗ 📂table
┣ 📂interfaces
┃ ┗ 📂table.ts
┣ 📜table.selectors.ts
┣ 📜table.thunk.ts
┗ 📜table.slice.ts
Here’s the table with coherent generic naming for a new service category:
| Concept | Existing Specific Name | Generic Name for New Category |
|---|---|---|
| AsyncThunk / action | modify | newCategoryService |
| Single service instance | modifier | newCategory |
| Collection of services | modifiers | newCategories |
| Operation / execution | modification | newServiceOperation |
Example: Modifiers as new Category Service
Here’s how the new Category Service appears in the frontend:
The form dynamically renders all fields provided by the service and can be used directly by end users.